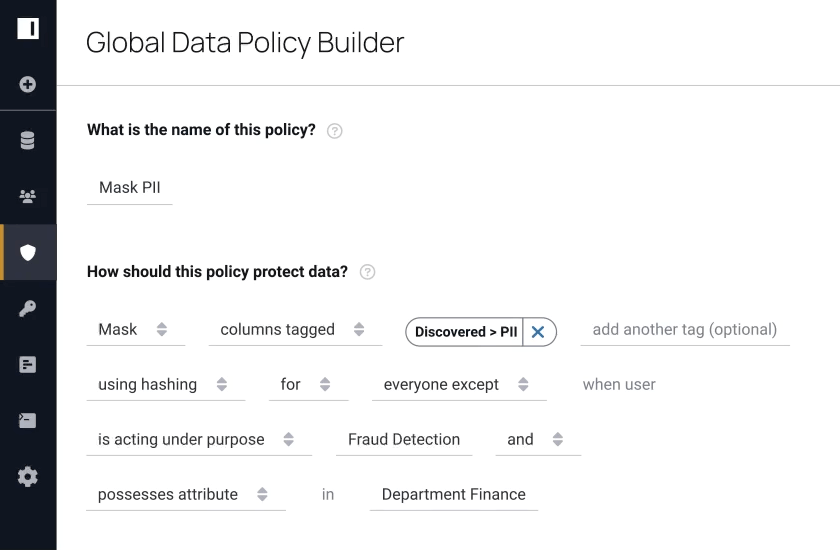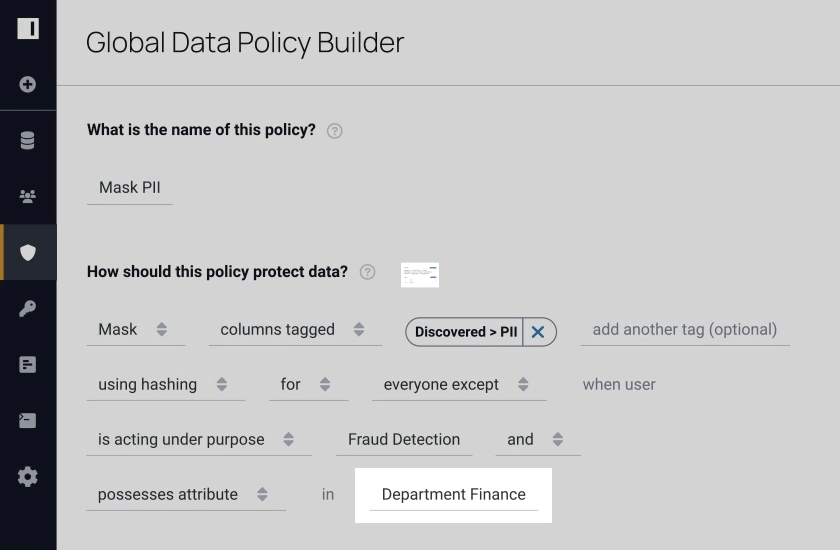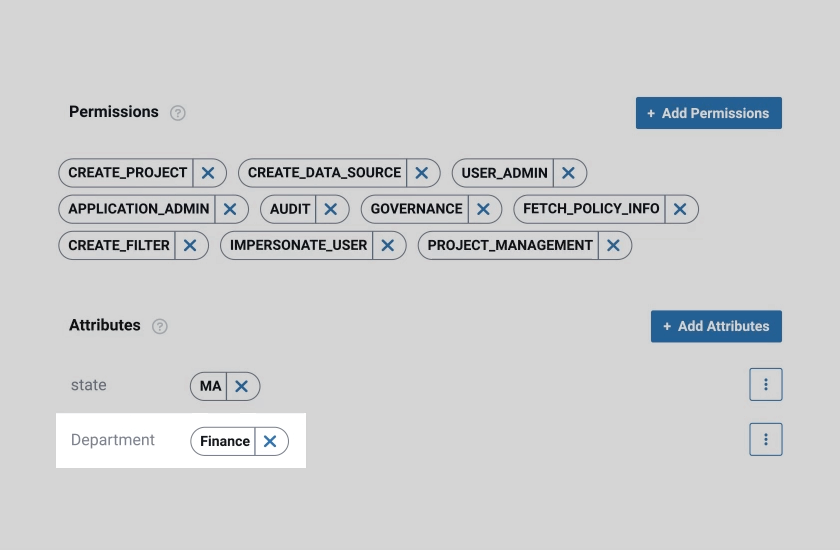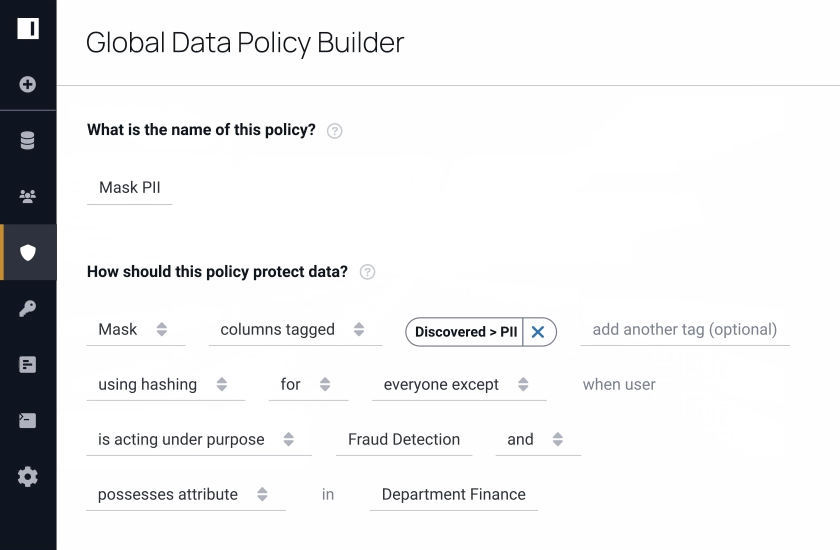
Our aim was to create more intelligent access control with greater efficiency. This was only possible through an advanced implementation of access control, which facilitates a higher degree of automation and transparency.
Covering the Full Data Security Spectrum
Ready to enforce data security and access controls, but not sure where to start?
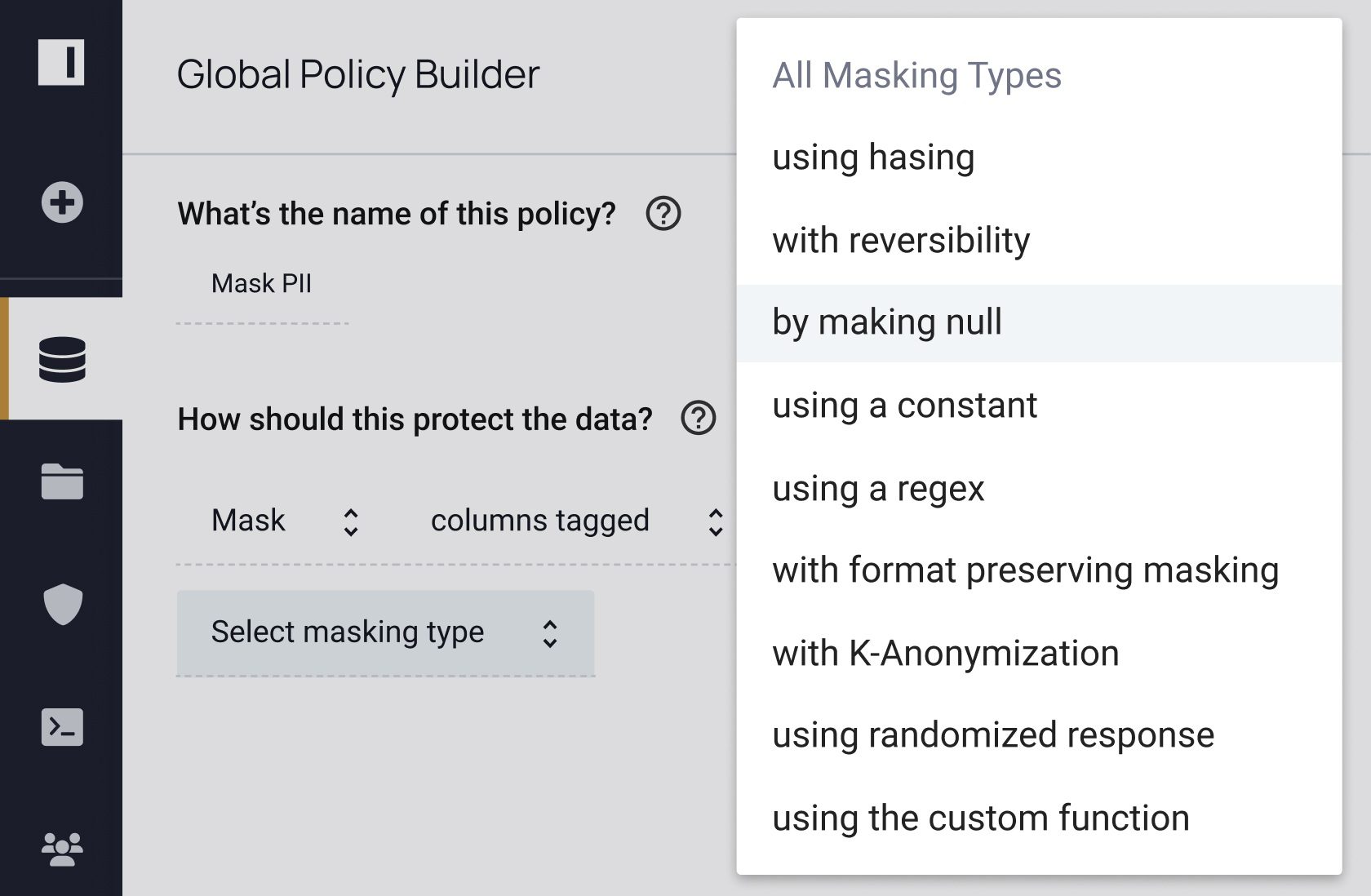
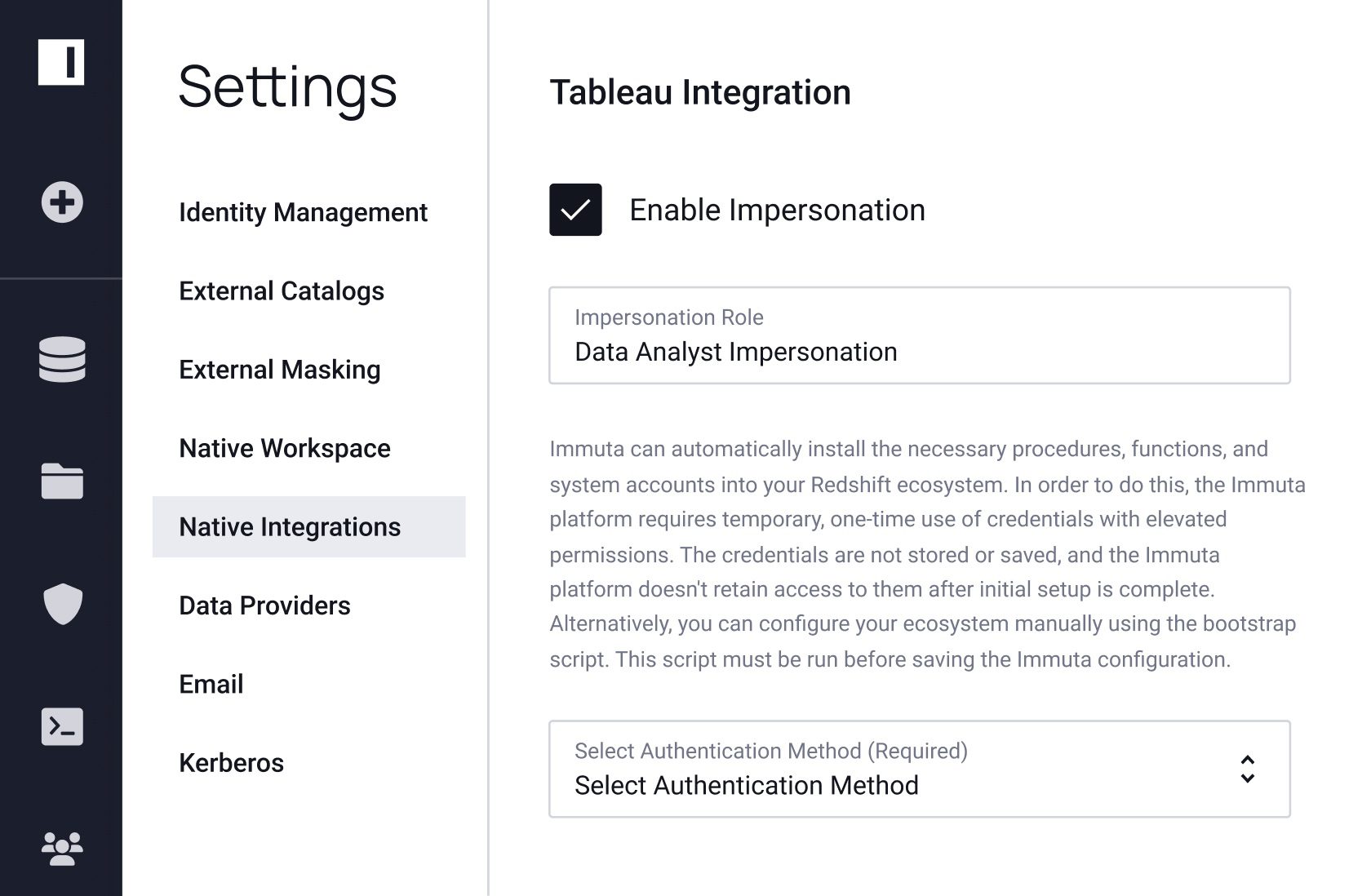
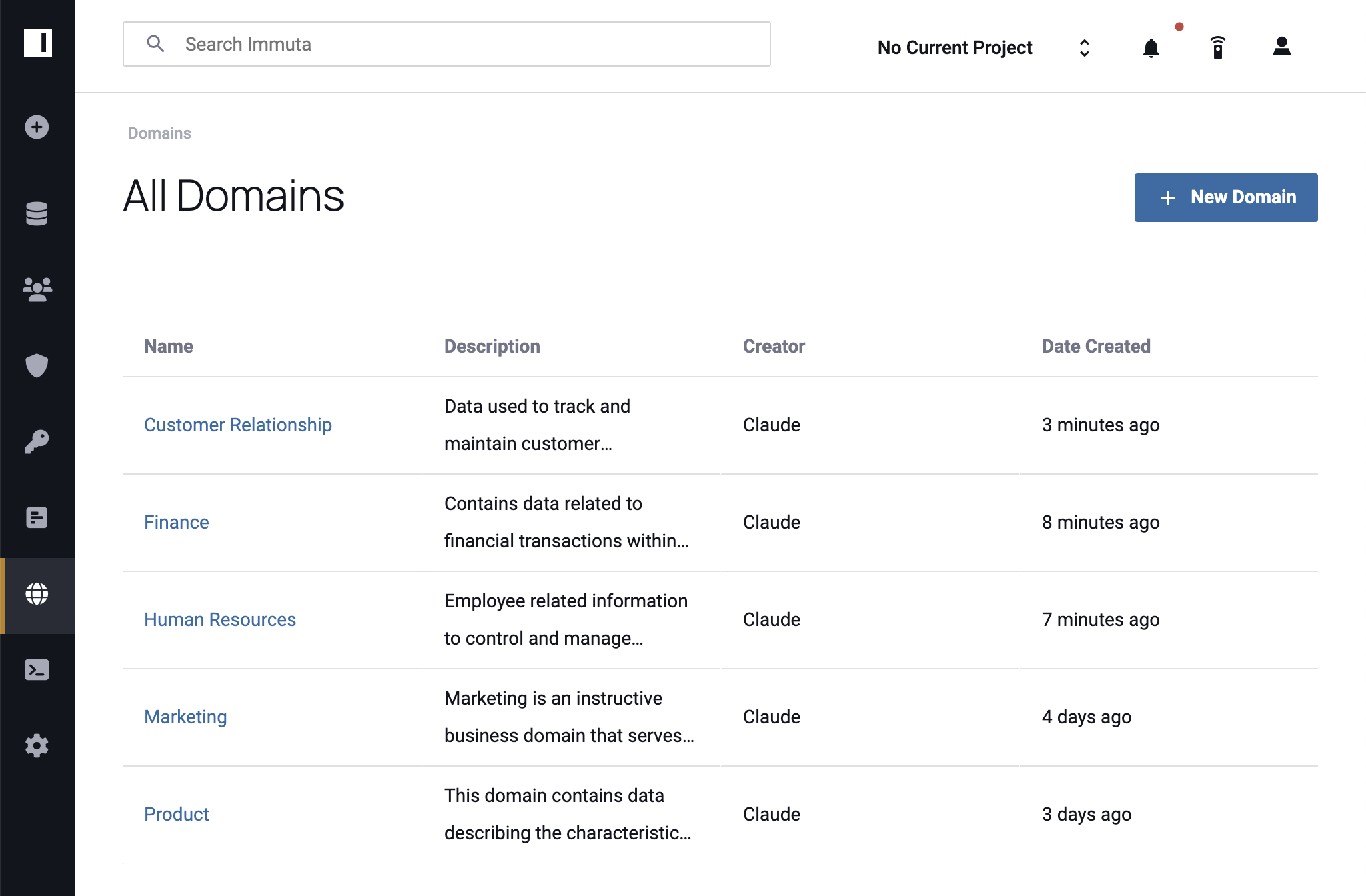
Knowing what sensitive data you have, where it resides, and how it is being accessed and used can help pinpoint potential risks, so you can put the right access controls in place to protect it. Immuta makes sure you can easily do it all – without sacrificing speed, utility, or security.