Historically, Amazon Web Services (AWS) was primarily the domain of data engineers who were best equipped to manage its complex methods of provisioning data access and services. However, a broader range of users are demanding access to data and leveraging AWS for analysis in Amazon Athena, EMR, Redshift, or directly from S3 blobs.
While this shift can vastly improve decision-making and innovation, it also means that data governance teams must be prepared to govern and provision more data – much faster and at a much greater scale. And, they need to do so without becoming a bottleneck or letting any sensitive information fall through the cracks.
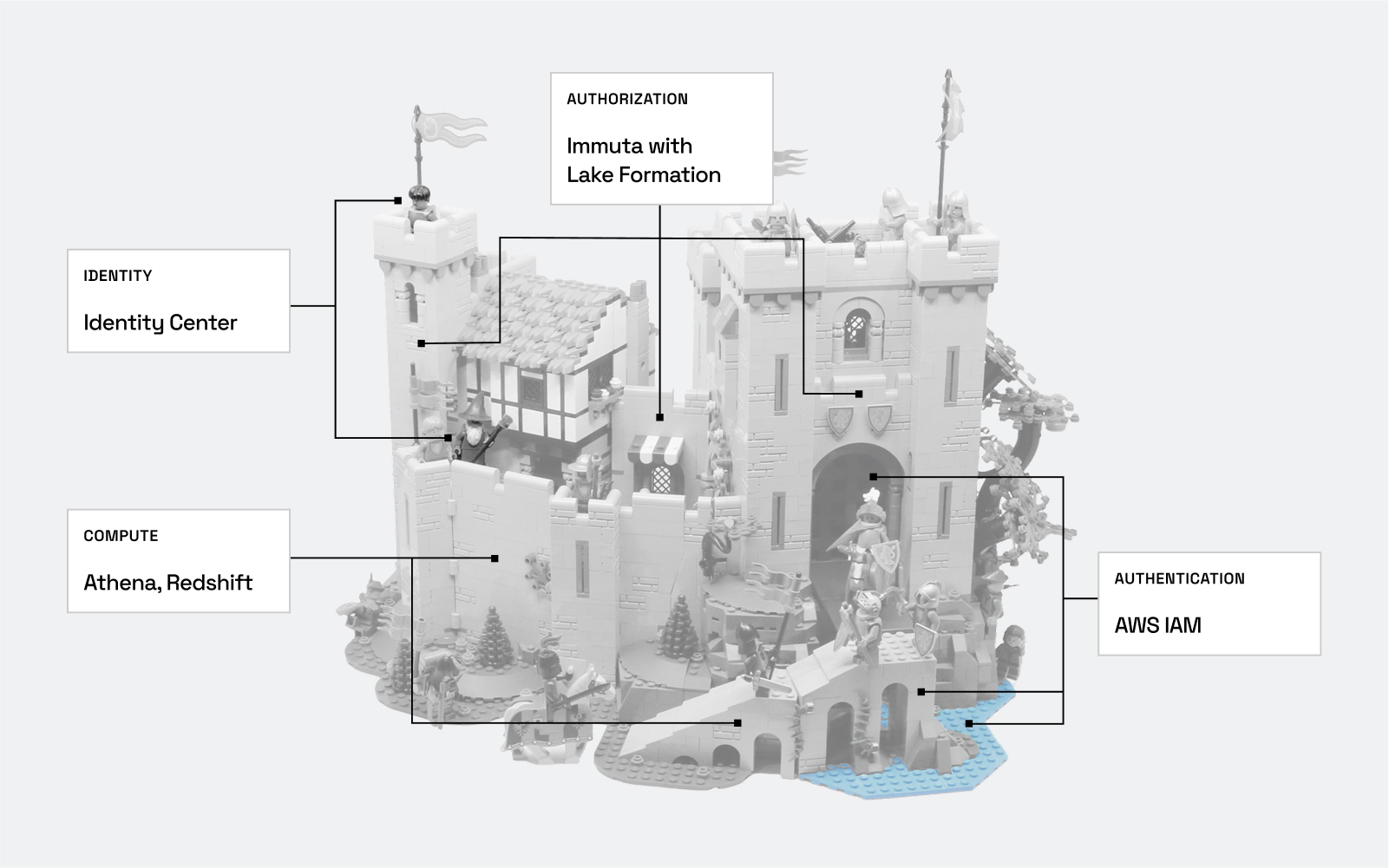
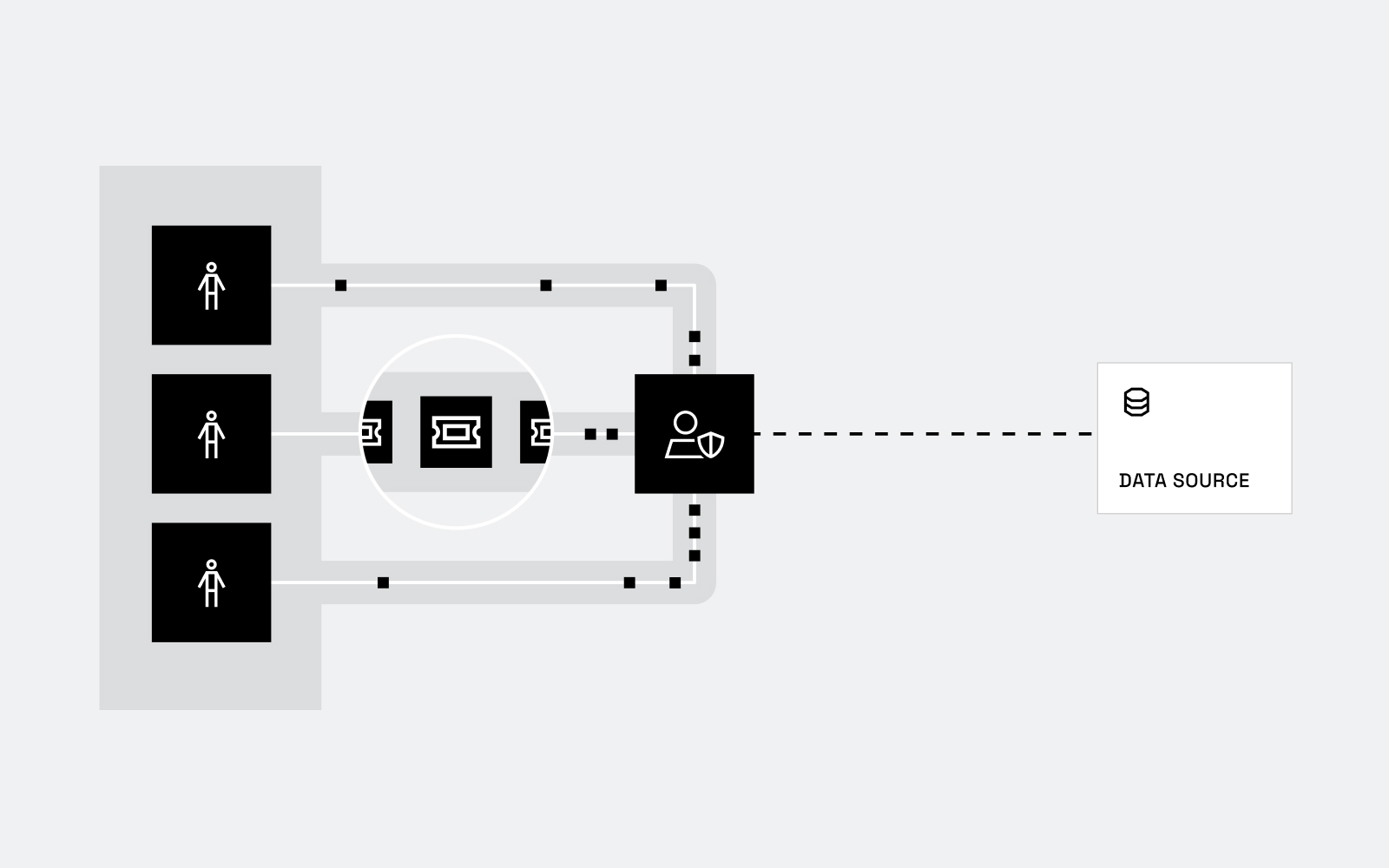
Immuta helps close the gap between speed and security, empowering organizations to optimize their AWS investments by automating data governance and provisioning. If AWS was a castle with data stored in various treasure chests, Lake Formation would be the keys, and Immuta would be the guard – making sure the right chests are in the right places and keys available to the right people.
This guide will demonstrate how Immuta integrates with AWS Lake Formation to securely automate access to these valuable resources – with no tickets, no delays, and no compromises.
For those who prefer visual learning, a demonstration video is available at the end of this guide.
What is AWS Lake Formation?
AWS Lake Formation is a service that allows you to easily create, govern, and manage data lakes by collecting, classifying, and refining data. The data can then be used for analytics, machine learning, and other advanced workloads.
Lake Formation’s power lies in its ability to integrate with various AWS services like Amazon S3 for storage, Amazon Athena for querying, and Amazon Redshift Spectrum for analytics, providing a centralized control plane for data lake security and operations.
Managing data access with native Lake Formation controls
Traditionally, managing permissions in an AWS data lake was complex, requiring you to manually configure S3 bucket policies and IAM roles. This was not only inefficient, but it also opened the door to inconsistent policy enforcement, outdated roles, and security blind spots.
Lake Formation streamlines these manual processes by offering a fine-grained security model built on top of the AWS Glue Data Catalog. This allows administrators to define permissions at the table, column, and even row level, granting access to specific data elements rather than entire datasets. From a regulatory compliance standpoint, this is crucial for ensuring that users only see the data they are authorized to access.
Recent developments in Lake Formation’s data access controls have focused on enhancing flexibility and integrations with other AWS services. For instance, users are now better able to define and enforce permissions across different data sources and analytical engines within the AWS ecosystem. These advancements aim to further simplify data lakes’ security posture, making it easier to manage access for a diverse set of users – from data analysts to machine learning engineers – while maintaining a strong security foundation.
Still, while DIY Lake Formation deployments are powerful, they often necessitate manually configuring user permissions at various levels. As data volumes grow and user needs evolve – particularly with the rapid adoption of AI – this approach will quickly become unwieldy and difficult to manage at scale.
To keep up, forward-looking and fast-moving organizations need another solution. Enter Immuta.
Why use Immuta to orchestrate Lake Formation?
As organizations aim to accelerate insights and improve collaboration across AWS services, they need to balance speed and agility with security and control. Immuta stands out as the optimal solution for automating AWS Lake Formation primitives due to its ability to dynamically manage both coarse-grained and fine-grained access. This allows you to easily grant the right permissions to any user without additional time or overhead.
By providing an automated, policy-driven approach, Immuta abstracts away the complexity of manually configuring permissions. Instead of directly manipulating Lake Formation’s underlying primitives (such as grants on databases, tables, or columns), you can define policies in Immuta that are automatically translated into the necessary Lake Formation permissions. This means that changes in Immuta to user attributes (e.g., group membership, department) or data classifications (e.g., tagging data as sensitive) are instantly reflected in Lake Formation, ensuring consistent and compliant access without manual intervention.
The dynamic nature of Immuta’s integration with Lake Formation is particularly beneficial for organizations operating at a large or growing scale. That’s because Immuta allows you to delegate data access management directly to data stewards and subject matter experts – the people who are closest to the data.
Let’s look at an example:
- A data steward overseeing a sensitive customer demographic dataset publishes it to the Immuta Data Marketplace, making it discoverable for analysts.
- When an analyst requests access to a specific project, the data steward approves it through the Marketplace, applying pre-defined Immuta policies that automatically enforce data masking or row-level filtering based on the analyst’s role or project scope.
- Crucially, once the project is completed or the analyst’s access is no longer required, the data steward can revoke access directly within the Marketplace.
- Immuta will automatically de-provision the corresponding Lake Formation permissions, ensuring that access is removed swiftly and preventing lingering security vulnerabilities, all without needing to involve a data engineer.
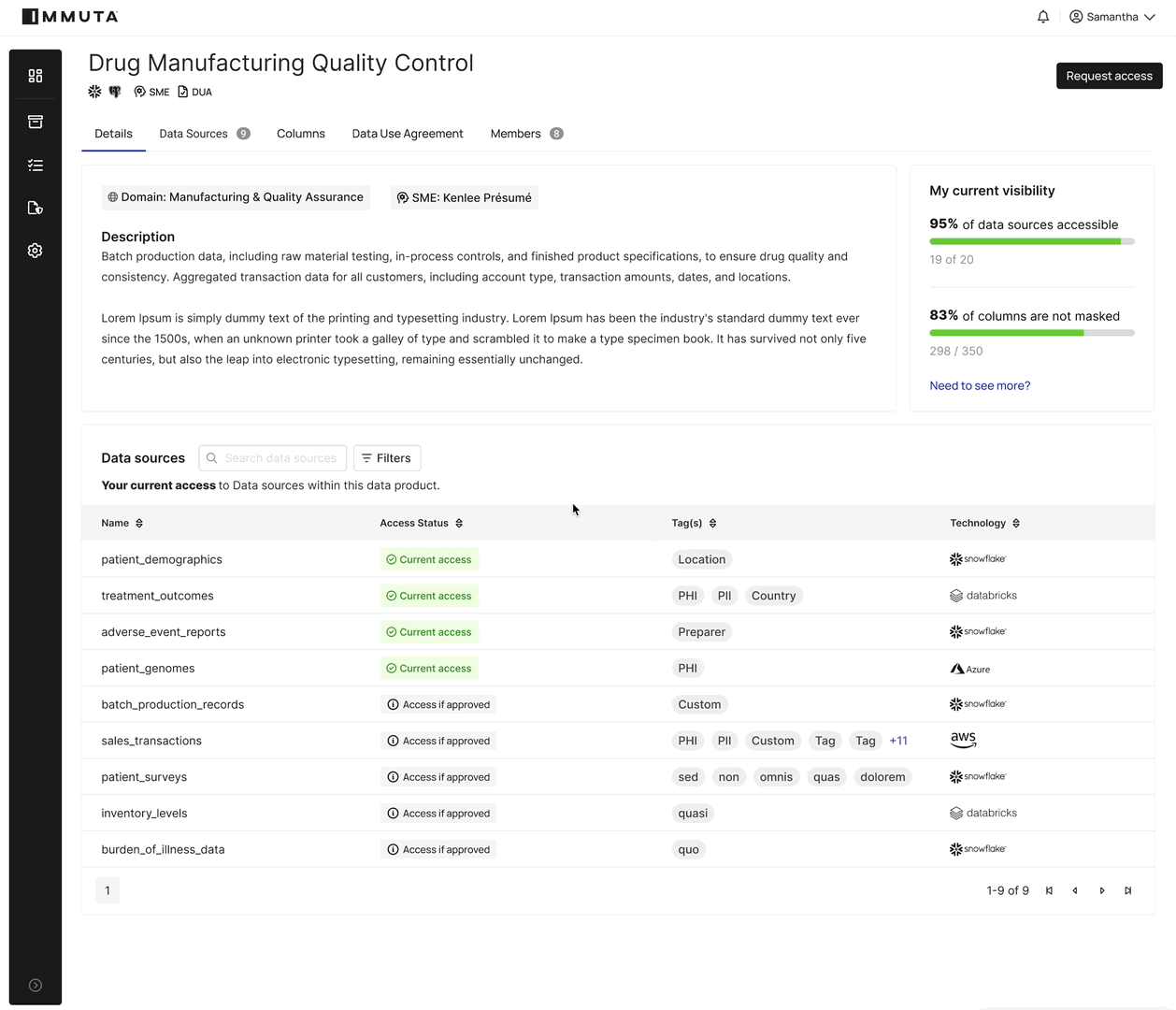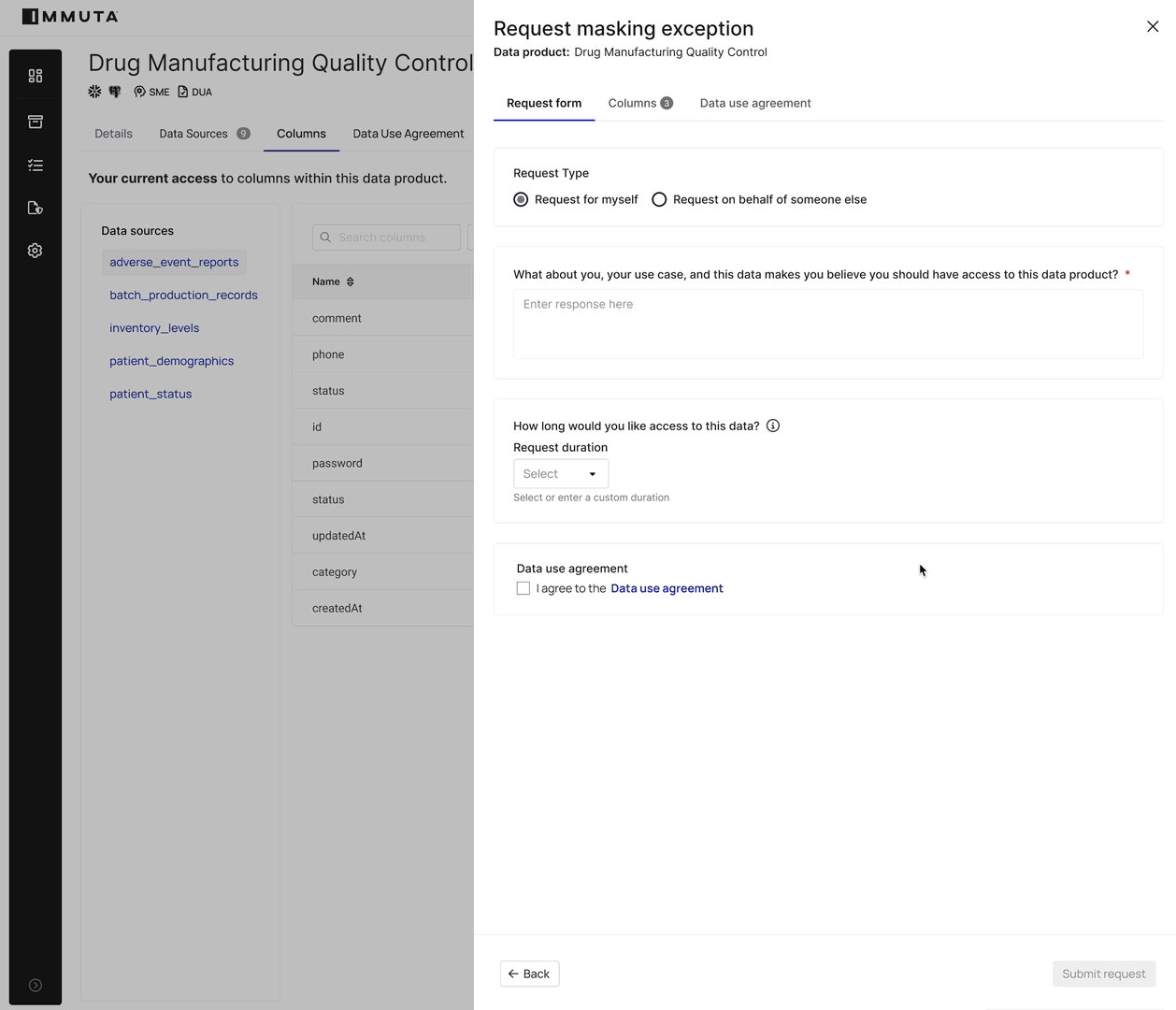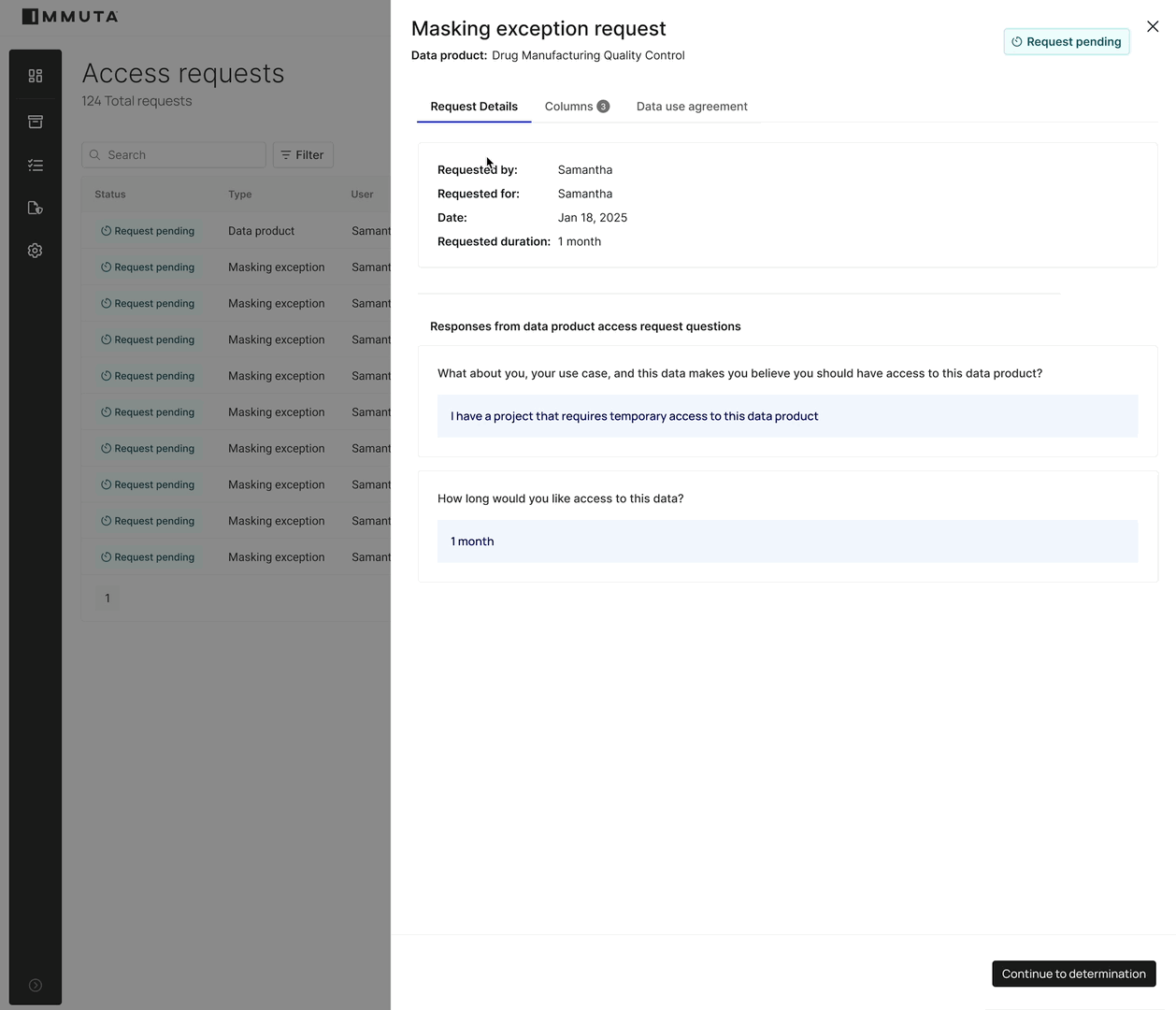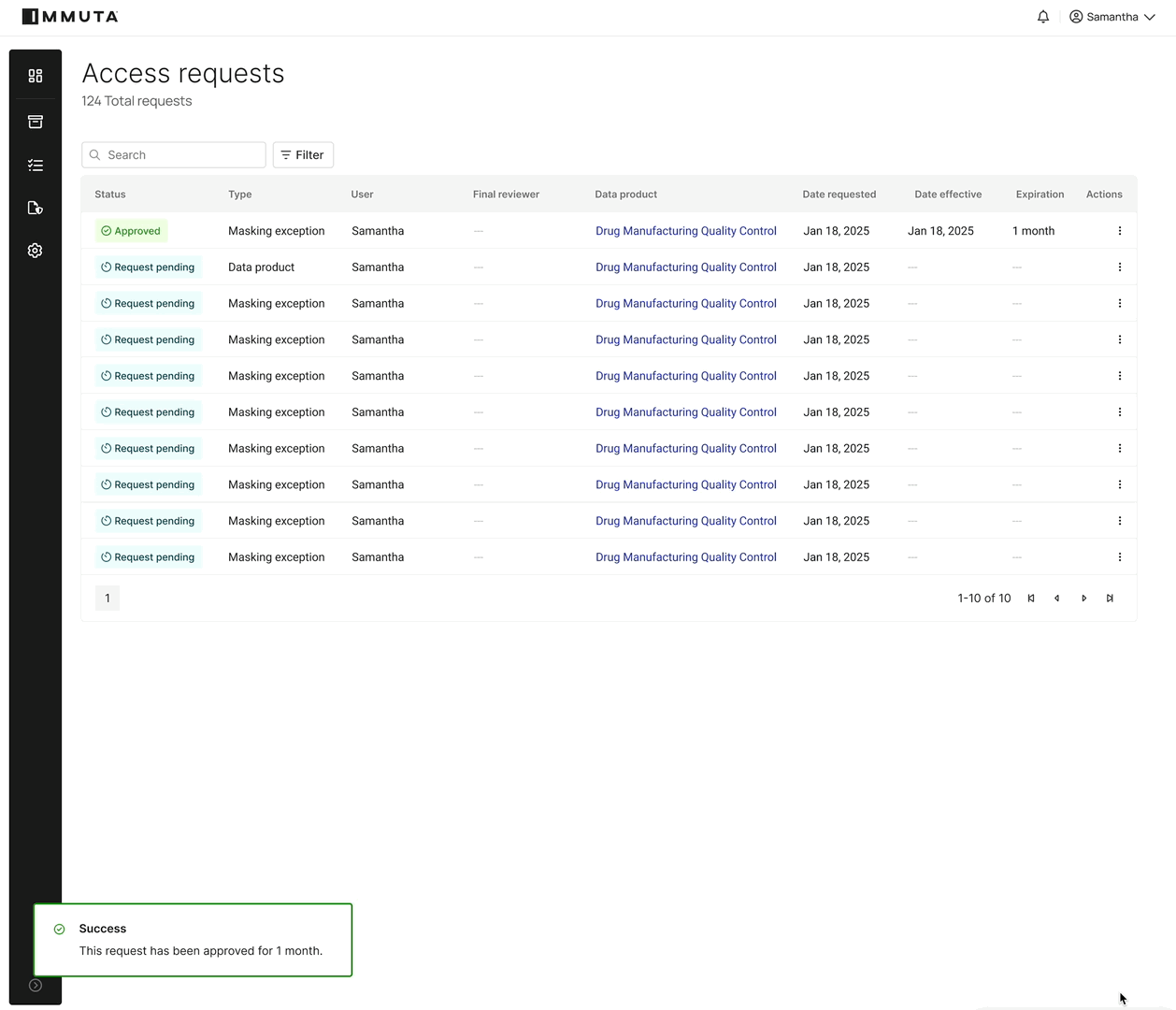
By providing a centralized, human-readable source of truth for access, Immuta enables data owners and stewards – even those without deep AWS expertise – to define and enforce access controls.
This self-service capability, combined with Immuta’s ability to dynamically push these policies down to Lake Formation’s granular security model, ensures that data access is always up to date and compliant. It shifts the focus from managing individual permissions to defining overarching data governance rules, allowing organizations to provision data access at scale while maintaining rigorous security and regulatory adherence.
This is an important step forward in Immuta’s ability to provision data across all leading cloud platforms, and we’re excited to see the continued expansion of the Lake Formation security model into more AWS services.
How would you do this without Immuta?
For organizations committed to a DIY approach, a well-trained technical staff can certainly learn and manage Lake Formation primitives to manually keep data access provisioning up to date. This involves:
- A deep understanding of AWS Glue Data Catalog, IAM roles and policies, and Lake Formation’s grant/revoke permissions.
- Data engineers who are proficient in crafting and applying fine-grained access controls at the database, table, column, and even row levels directly within the Lake Formation console or via programmatic APIs.
- Meticulous attention to detail and ongoing education as AWS services evolve.
However, scaling this manual process presents significant challenges. As data estates grow and user needs diversify, the volume of access requests can quickly overwhelm even dedicated teams.
A common workflow involves a ticketing system where data consumers submit requests for access. These tickets are then routed to a team of data engineers, who, by necessity, often possess extensive levels of access to the data lake environment to fulfill these requests. While this ensures that requests are eventually addressed, it can create a bottleneck, as engineers are pulled away from more strategic, interesting problems like optimizing data pipelines or developing new analytical capabilities.
Additionally, manually managing permissions through a ticketing system can introduce auditability concerns. Tracking who granted what access, when, and why becomes a complex task – especially as data volumes and users grow – making it difficult to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements. The sheer volume of individual grants and revocations can lead to human error, potentially creating security vulnerabilities or inadvertently restricting legitimate access.
Data engineers, while capable of the task, would generally prefer to apply their expertise to innovative solutions rather than the repetitive and audit-intensive work of manual access provisioning.
What does Immuta’s Lake Formation integration look like?
Let’s look at Immuta’s integration with Lake Formation.
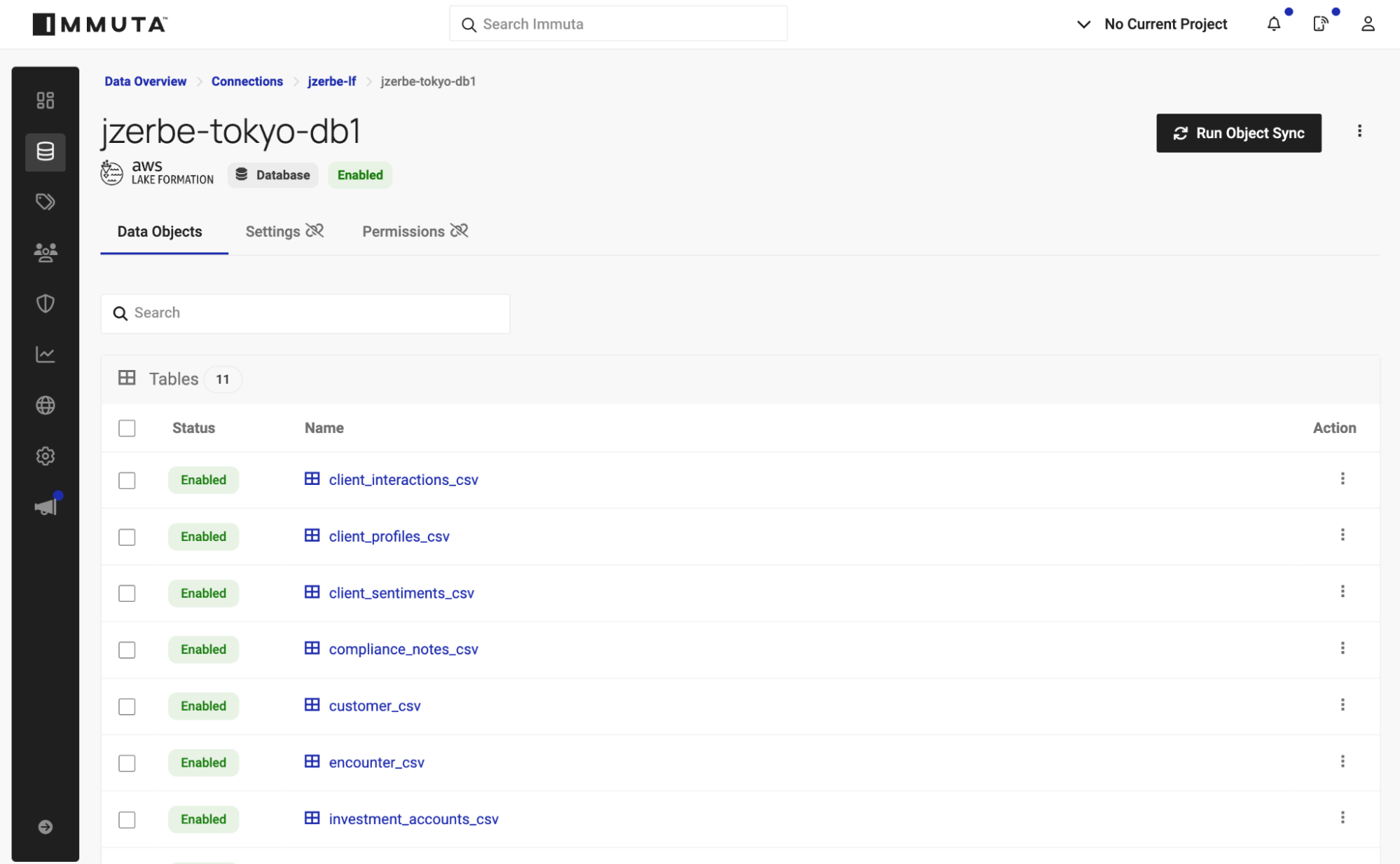
All new integrations are available with Immuta’s onboarding process called Connections, which provides a familiar instance->database->schema->table view of data assets.
Upon further inspection into the customer_csv table, we notice that this newly crawled Glue table is automatically tagged with the database it’s from, as highlighted in red below.
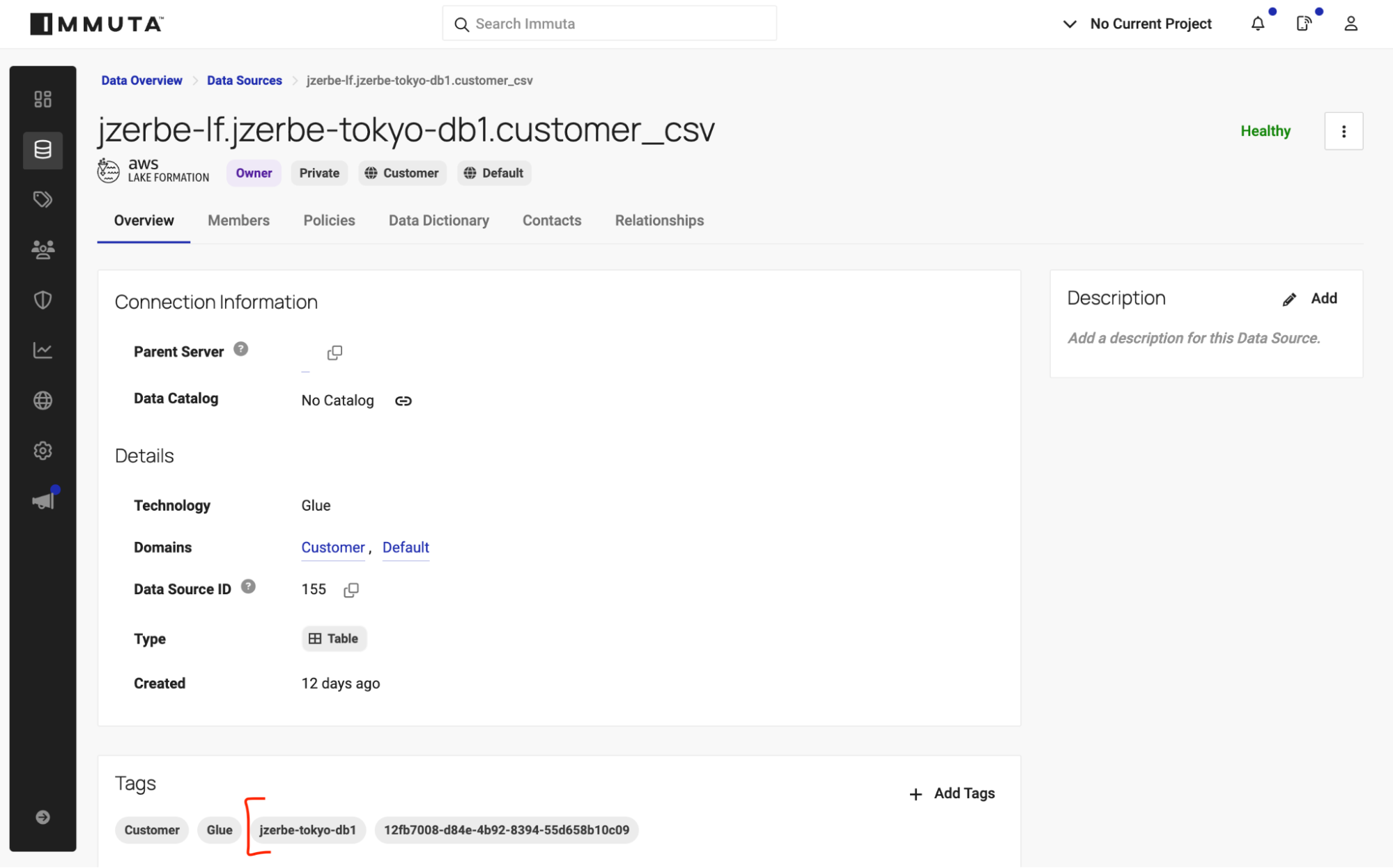
Many of Immuta’s customers use a similar approach, building policies based upon table tags.
How to connect Lake Formation to Immuta
Interested in orchestrating Lake Formation access with Immuta policy? In the following demo, we’ll show you how to:
- Connect a Lake Formation region
- Select relevant data sources
- Provision access to specific schemas and tables
Learn more.
Experience Immuta + AWS Lake Formation.











