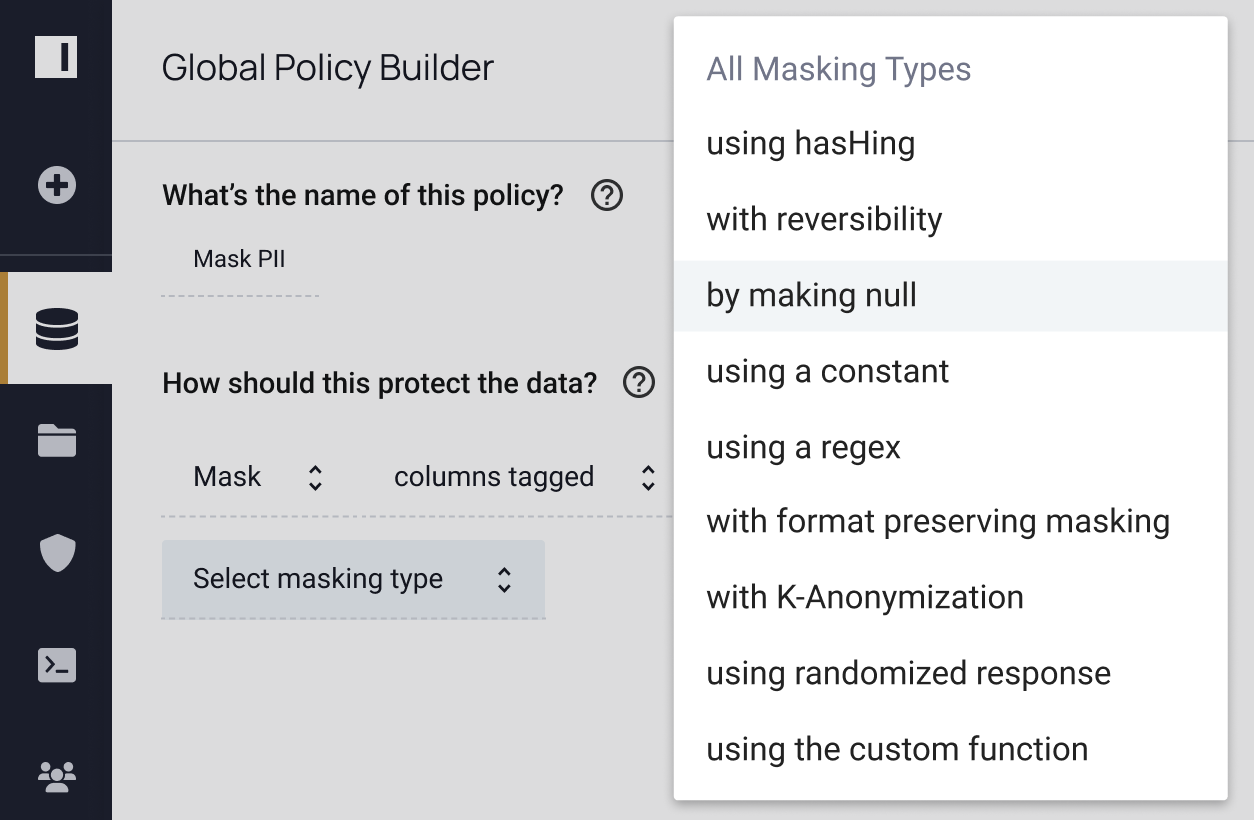
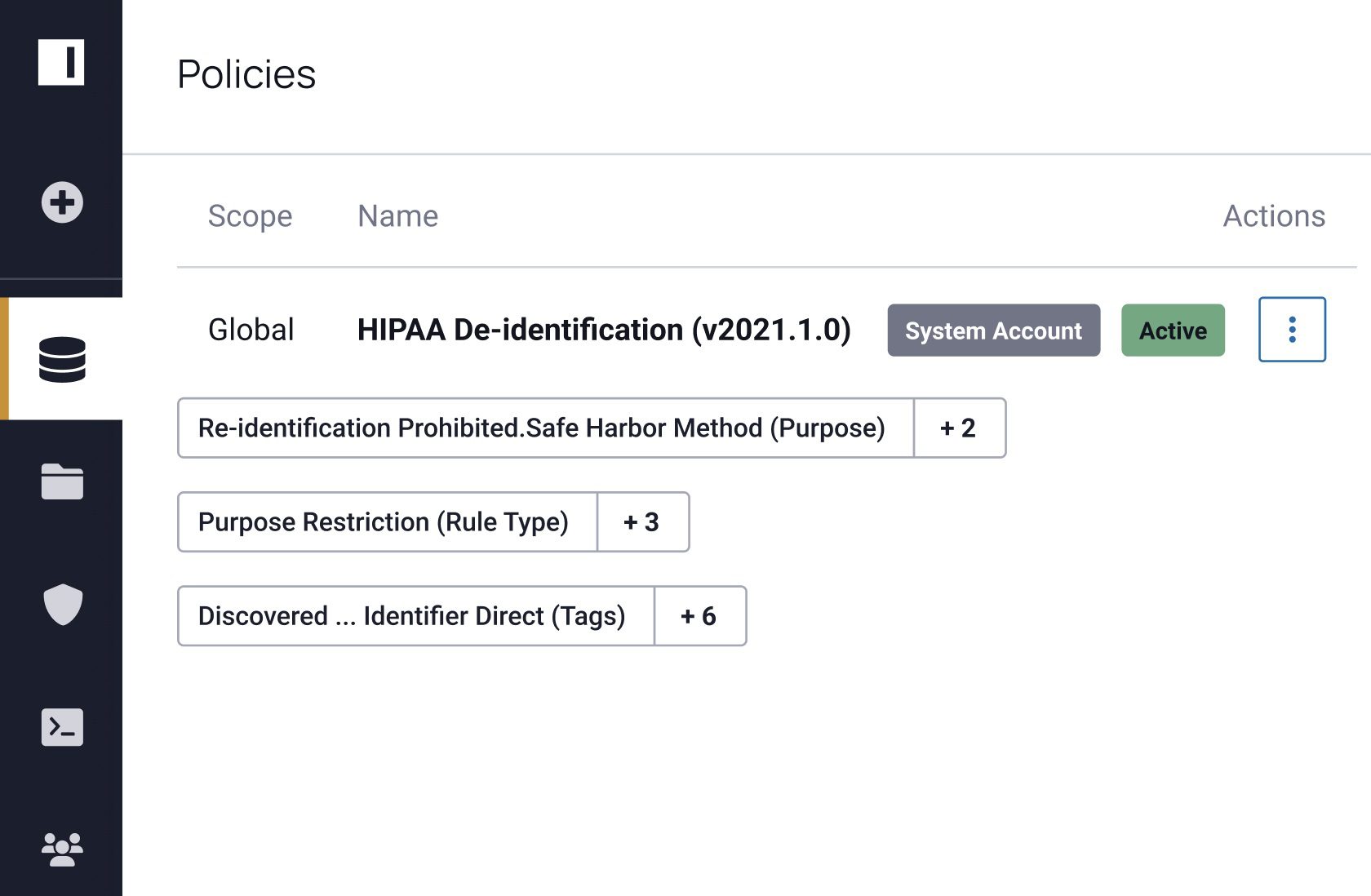
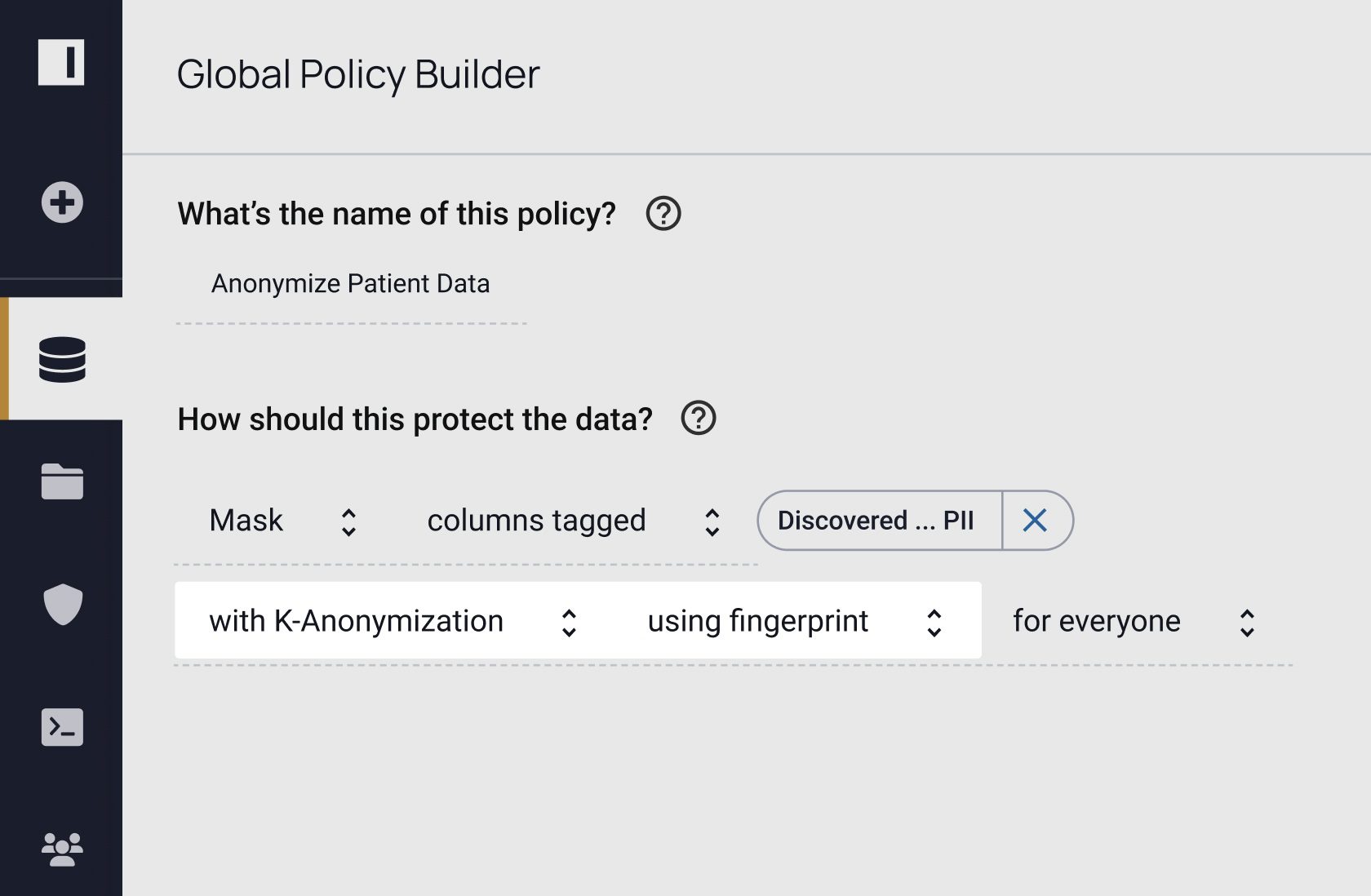
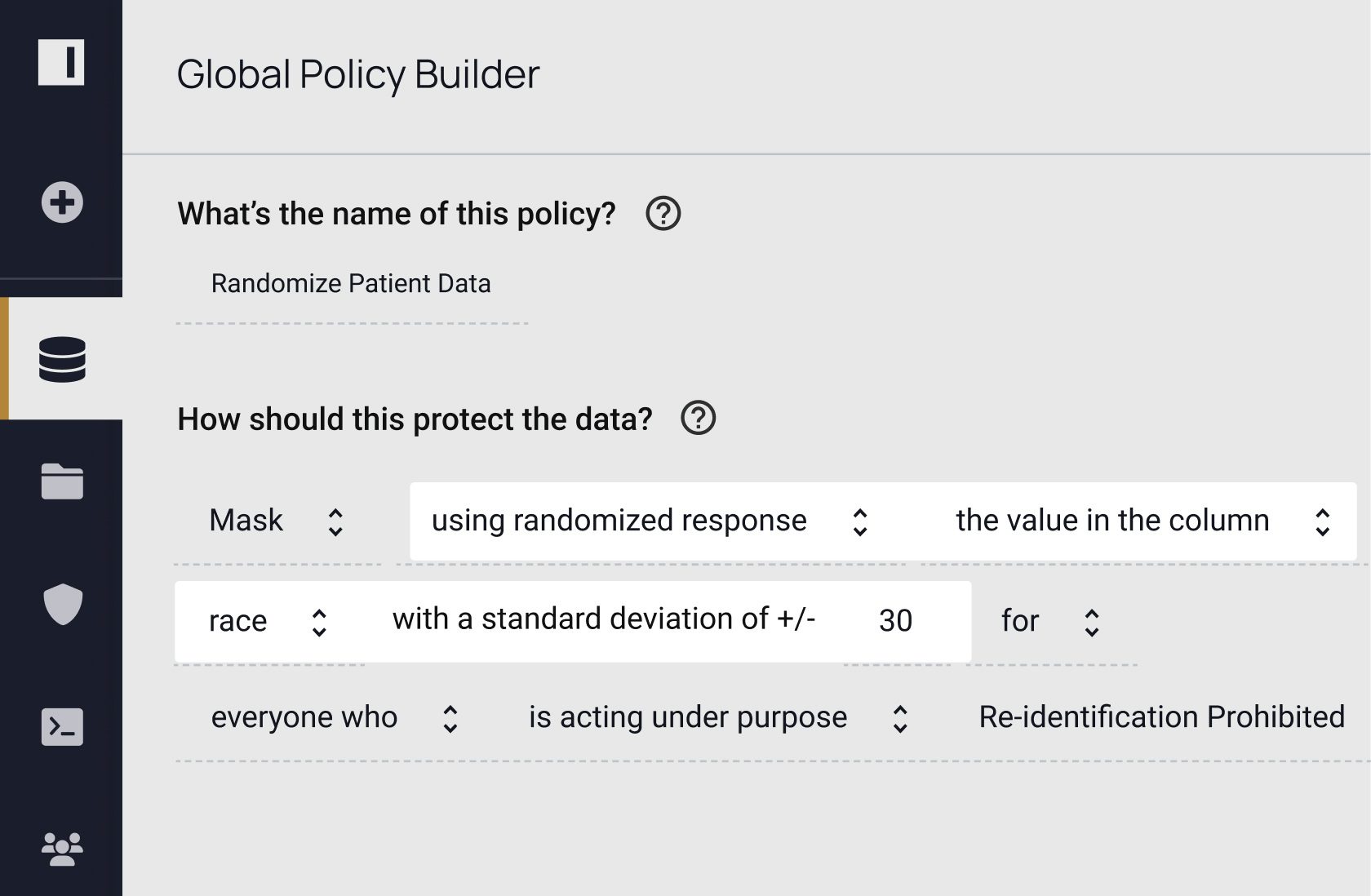
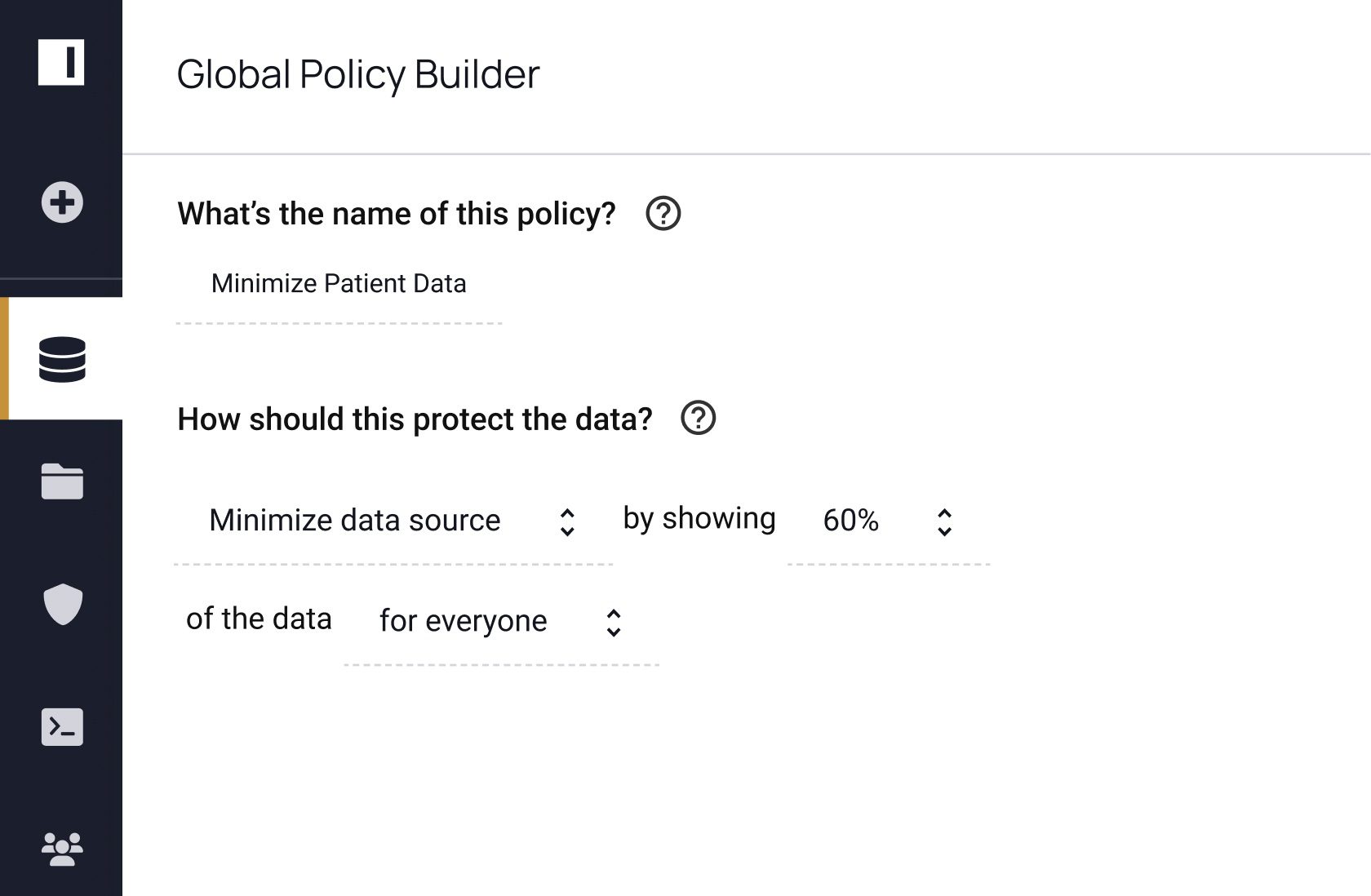
"We’re looking at anonymization of data through the privacy enhancing techniques that Immuta provides, including different accelerators and adding a query layer or data dictionary. These are the primary areas of focus on our roadmap."
Covering the Full Data Security Spectrum
Privacy enhancing technologies help ensure your data is protected, but you still need to know where to apply them and verify their efficacy. Immuta provides full data security coverage by allowing you to discover, secure, and monitor data usage to detect risks. See how you can do all three – without sacrificing speed or utility.